North Dakota Carbon Capture Opportunities

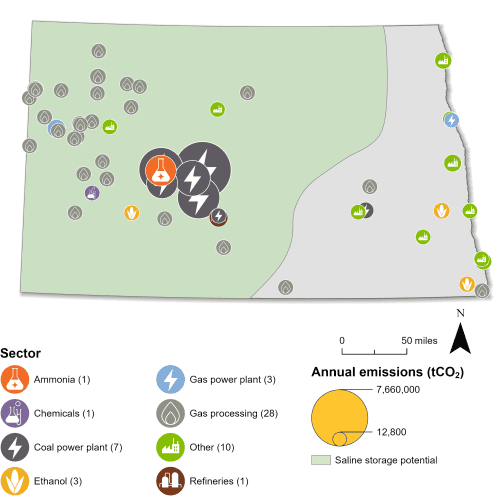
Carbon management technologies can lower emissions across a variety of sectors in North Dakota and bring jobs and private investment to the state. Of North Dakota’s 64 industrial and power facilities, 57 are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. The state’s highest emitters are its seven coal power plants, all of which are 45Q-eligible. These seven coal plants emit nearly 25 million metric tons of CO2 annually, representing roughly 74 percent of the state’s total annual CO2 emissions.
North Dakota was the first state to obtain Class VI primacy, and to date has issued Class VI permits to nine facilities. The state also has several laws in place and has added additional measures during recent legislative sessions to create a favorable environment for carbon management deployment. Additionally, former Governor Doug Burgum set a goal of achieving carbon-neutral status by 2030 and frequently highlighted carbon management as a promising solution to attain reliable and affordable energy while lowering emissions.

Industrial and Power Facilities in North Dakota
North Dakota has a total of 64 industrial and power facilities, 57 of which are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. The state’s highest emitters are its seven coal power plants, all of which are 45Q-eligible. These seven coal plants emit nearly 25 million metric tons of CO2 annually, representing roughly 74 percent of the state’s total annual CO2 emissions. Additionally, North Dakota has 31 gas processing plants, three gas power plants, three ethanol plants, one ammonia facility, and 12 other facilities that are eligible for the 45Q tax credit. In total, CO2 emissions from all 57 facilities represent 99 percent of the state’s overall annual CO2 emissions.
In addition to CO2 capture, North Dakota has significant capacity to safely store CO2 underground in geologic storage formations. It is one of four states with Class VI primacy, alongside Wyoming, Louisiana, and West Virginia. To-date, the state has issued Class VI permits to nine facilities. North Dakota is also well-positioned as a corridor for transporting CO2 regionally.
Active carbon management projects in the state include Gevo’s low-carbon ethanol production facility and Project Tundra, a collaboration between Minnkota Power Cooperative, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Kiewit, and the Energy and Environmental Research Center at the University of North Dakota.
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024. Bauer et al., NATCARB, 2018.
Legislative Context for Carbon Management
North Dakota has developed a supportive environment for carbon management, and current legislation has encouraged further investment and innovation. In 2021, North Dakota enacted House Bill 1452, which called for the allocation of $25 million over the following two years to accelerate clean, sustainable energy investment. The bill also established a Clean Sustainable Energy Authority to advise the state’s Industrial Commission and provide oversight on sustainable energy projects and funds. In the same session, the state passed Senate Bill 2152 to increase sales and use tax exemptions for the secure geologic storage of CO2, and Senate Bill 2206 allowed utilities to “recover its research and development costs incurred to develop lignite more cleanly, efficiently, or economically, including carbon dioxide capture and sequestration utilization.”
Notably, former Governor Doug Burgum frequently voiced his support for carbon management. During his term, he set a goal of achieving statewide carbon neutrality by 2030 and promoted an “all-of-the-above” approach to advance domestic clean energy production and become the nation’s first carbon-negative state.
Most recently, North Dakota enacted two bills in the 2025 session related to carbon management deployment:
- SB 2333: Established a Low-Carbon Fuels Fund aimed at promoting low-carbon fuel initiatives. This fund provides financial incentives for ethanol production facilities undertaking eligible capital projects that reduce their carbon intensity. The incentives cover up to 50% of project costs, with a cap of $3 million per two years and a cumulative limit of $10 million per facility over a ten-year period. Eligible projects include infrastructure for carbon capture and storage.
- HCR 3016: Recognized the economic and energy security benefits of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and urged the State of North Dakota and the federal government to maintain policies that support the development of carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies. The resolution asks the federal government to incentivize CO2 utilization for EOR and strengthen partnerships with North Dakota’s energy sector.
The 2025 North Dakota legislative session adjourned on May 2, 2025, with several additional carbon management-related bills failing to pass. To review the contents of these bills, view our 2025 State Legislative Tracker.
This bubble diagram shows the number of facilities and corresponding annual CO2 emissions for each industry in North Dakota. The darker large bubbles are eligible for the 45Q carbon capture tax credit, while the faded bubbles are too small to be eligible. The total amount of CO2 emissions in North Dakota is listed for each industry.
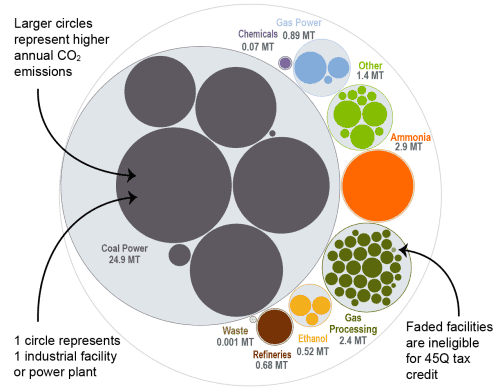
Source: EPA GHGRP, 2024.
Last updated: June 2025

