Mississippi Carbon Capture Opportunities

Carbon management can lower emissions across a variety of sectors in Mississippi and bring jobs and private investment to the state. Of the 112 industrial and power facilities in the state, 83 are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. These 83 facilities emit about 43 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) annually, representing 99 percent of total annual CO2 emissions in the state.
Mississippi has passed some legislation surrounding carbon management. However, expanding the legislative and regulatory framework through the enactment of additional supportive policies can create greater clarity and stability for carbon management deployment in the state.

Industrial and Power Facilities in Mississippi
Carbon management could play an important role in decarbonizing Mississippi’s industrial and power sectors, with 83 facilities that are 45Q-eligible. The state’s 21 gas power plants account for the highest proportion of annual CO2 emissions, and 20 of these plants are 45Q-eligible. Mississippi also has a significant pulp and paper industry, and all four of its pulp and paper plants are eligible. In fact, it was announced in 2024 that International Paper’s containerboard mill in Vicksburg, Mississippi received US Department of Energy funding to develop a carbon capture pilot at the facility.
The state also has 32 gas processing plants, five chemicals facilities, three refineries, two steel plants, and 17 other eligible facilities. In total, emissions from all 83 eligible facilities represent 99 percent of Mississippi’s total annual CO2 emissions.
Beyond capture, Mississippi has potential to safely store CO2 underground in geologic formations. As such, the state submitted a letter of intent to apply for funding under the US Environmental Protection Agency’s Underground Injection Control (UIC) Class VI grant program in 2023. This grant program was developed to help states prepare for Class VI primacy, which gives individual states primary permitting authority over their Class VI injection wells.
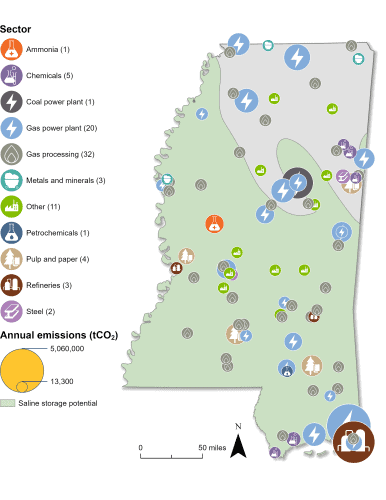
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024. Bauer et al., NATCARB, 2018.
Legislative Context for Carbon Management
Mississippi has introduced several pieces of legislation in recent years related to the regulation of carbon management technologies. The legislature introduced HB 1037, or the Mississippi Geologic Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide Act, in 2021. This bill would have granted the State Oil and Gas Board with jurisdiction and authority over the geologic storage of carbon dioxide. It also declared that CO2 storage will benefit the citizens of Mississippi and its environment and defined CO2 as a commodity, but the bill died in committee. The issue was taken up again in the subsequent legislative session, and the Mississippi State Legislature enacted HB 1214 in 2022. Also within this bill are provisions noting the state’s intent to apply for Class VI primacy and clarity on requirements for seeking unitization (including majority agreement among surface and underground owners).
More recently, the state enacted SB 2059 in 2024, which classified bioenergy from biomass as carbon-negative when paired with carbon capture and storage. In 2025, the legislature introduced two bills related to carbon management, but both died in committee. To see details of these bills, view our State Legislative Tracker.
This bubble diagram shows the number of facilities and corresponding annual CO2 emissions for each industry in Mississippi. The darker large bubbles are eligible for the 45Q carbon capture tax credit, while the faded bubbles are too small to be eligible. The total amount of CO2 emissions in Mississippi is listed for each industry in million metric tons.
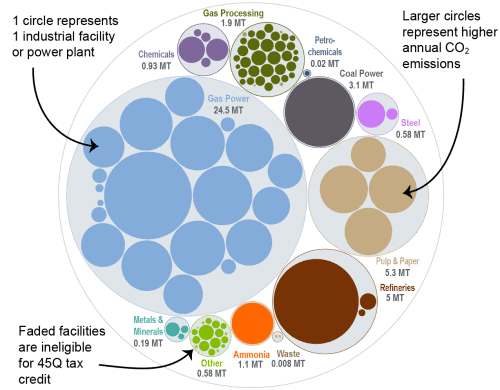
Source: EPA GHGRP, 2024.
Last updated: June 2025

