Minnesota Carbon Capture Opportunities

Carbon management could play a key role in Minnesota’s emissions reduction efforts and clean energy goals. Of the 123 industrial and power facilities in the state, 100 are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. At 18 plants, gas power makes up the highest proportion of these facilities. The ethanol industry also plays a prominent role in the state’s economy and has 18 eligible facilities. In total, all 100 of the state’s 45Q-eligible facilities emit nearly 36 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) annually, representing 99 percent of total annual CO2 emissions in the state.
Minnesota has set meaningful clean energy targets and has passed some legislation recognizing the potential of carbon management in the state. To further support deployment, Minnesota could benefit from passing additional legislation and establishing a clearer and more supportive regulatory framework around key issues.

Industrial and Power Facilities in Minnesota
Minnesota has 123 industrial and power facilities, 100 of which are eligible for 45Q. The state’s highest emitter is the coal power sector, and all three of Minnesota’s remaining coal plants are eligible for the tax credit. The state’s second-highest emitter, the gas power sector, has the highest proportion of facilities in the state, at eighteen, and all are 45Q-eligible. The ethanol sector also plays a prominent role in Minnesota’s industrial landscape, with 18 eligible facilities. The emissions from these three sectors alone represent nearly 60 percent of Minnesota’s total annual CO2 emissions. Additionally, Minnesota has 11 gas processing plants, 10 metals and minerals facilities, four pulp and paper facilities, and 37 other facilities that are 45-eligible. In total, the emissions from Minnesota’s 100 eligible facilities represent 99 percent of the state’s total annual CO2 emissions.
While Minnesota has limited potential to store CO2 in geologic storage formations, the state is well-positioned as a corridor for transporting CO2 regionally.
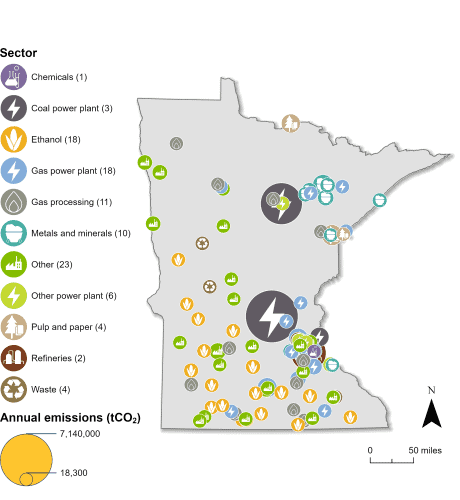
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024. Bauer et al., NATCARB, 2018.
Legislative Context for Carbon Management
Minnesota has set ambitious emissions reduction goals with both the Next Generation Energy Act, which set an 80 percent greenhouse gas reduction goal by 2050, along with the Minnesota Renewable Energy Standard, which requires Minnesota utilities to obtain at least 25 percent of their electricity from renewable sources by 2025. The state continues to build on its clean energy legislation with various proposals to move beyond existing clean energy requirements, some of which recognize the role of carbon capture in achieving 100 percent decarbonization of the electricity sector.
For example, in 2024, the state enacted legislation mandating an independent third-party study on CO2 pipelines to assess their human health and environmental impacts and to recommend regulatory measures. During the 2025 legislative session, several bills related to carbon management were introduced, but none were passed before session concluded.
This bubble diagram shows the number of facilities and corresponding annual CO2 emissions for each industry in Minnesota. The darker large bubbles are eligible for the 45Q carbon capture tax credit, while the faded bubbles are too small to be eligible. The total amount of CO2 emissions in Minnesota is listed for each industry.
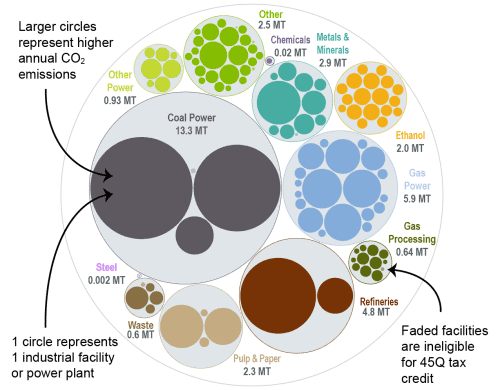
Source: EPA GHGRP, 2024.
Last updated: June 2025

