Michigan Carbon Capture Opportunities

Carbon management is poised to play a key role in Michigan’s emissions reduction efforts and clean energy goals. Of the 205 industrial and power facilities in the state, 142 are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. Most of the state’s gas and coal power plants are 45Q-eligible, and these plants alone represent about 74 percent of the state’s total annual carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Michigan’s other key industrial sectors, including steel, cement, and ethanol production, also present significant potential for emissions reductions through carbon management. Together, these 142 facilities emit around 66 million metrics tons of CO2 annually, representing 99 percent of total annual CO2 emissions in the state.
Michigan has taken meaningful steps in the last several years to lay a legislative foundation for carbon management deployment in the state. Most recently, the Michigan state legislature appropriated funds in 2024 to help the state obtain Class VI primacy and introduced a package of bills aimed at positioning Michigan as a national carbon management leader.
Industrial and Power Facilities in Michigan
Michigan has 142 facilities that are eligible for the 45Q tax credit. The plurality of these facilities are gas power plants, at 25. However, Michigan’s six coal power plants are its highest emitters, five of which are eligible for the 45Q tax credit (coal plants that are slated for imminent retirement are not included in these figures). Together, emissions from these power plants alone represent about 74 percent of Michigan’s total annual CO2 emissions.
Additionally, Michigan has 19 gas processing plants, 10 pulp and paper facilities, eight steel plants, four ethanol plants, four cement facilities, and 65 other facilities that are 45Q-eligible. In total, these 142 facilities emit approximately 66 million metric tons of CO2 annually, representing 99 percent of the state’s total annual CO2 emissions.
Michigan also has the potential to safely store captured CO2 underground in geologic formations. DTE Energy, one of Michigan’s largest electric utilities which has pledged net-zero carbon emissions by 2025, is currently partnering with Battelle on a federally funded project to develop an integrated commercial-scale storage complex capable of storing 63 million metric tons of CO2 in saline formations in the Southeastern region of the Michigan Basin. Currently, Michigan has two active Class VI well applications with the US Environmental Protection Agency. The state also submitted a letter of intent to apply for funding under the EPA’s Underground Injection Control Class VI grant program in 2023.
From 2003 to 2020, Michigan was a part of the Midwest Regional Carbon Sequestration Partnership, a project established to assess carbon capture potential, economic viability, and public acceptance of carbon storage. Through the group’s effective small-scale CO2 injection tests, the state was able to convene influential stakeholders to discuss and examine the future of carbon management in Michigan. In 2020, Michigan engaged in a new collaborative project called the Midwest Regional Carbon Initiative, which led additional carbon management research and planning.
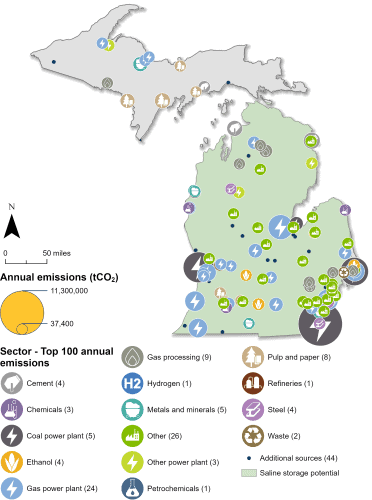
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024. Bauer et al., NATCARB, 2018.
Legislative Context for Carbon Management
HR 193, passed in 2015, urged Michigan’s government to support and explore policies related to carbon capture and storage. The study that resulted from this resolution found that state support, in addition to the federal 45Q tax credit, is necessary to deploy carbon capture technologies at scale. Michigan also enacted HB 5254 in 2014, allowing CO2 pipelines to be under the purview of the Michigan Public Service Commission for permitting and construction.
In 2024, Michigan enacted SB 0747, which appropriated funds to the Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE) to assist the state in obtaining Class VI primacy. Also in 2024, the Michigan Chamber of Commerce led a coalition effort to support legislation that positions Michigan as a national carbon management leader. Senate Bills 1131-1133 would create a permitting and regulatory structure for carbon capture facilities under EGLE. The bills would also create fee structures and other components, like a legacy fund, to ensure resources are available for future monitoring of carbon storage wells after a project reaches its end of life.
To stay updated on Michigan’s active carbon management legislation, view our State Legislative Tracker.
This bubble diagram shows the number of facilities and corresponding annual CO2 emissions for each industry in Michigan. The darker bubbles are eligible for the 45Q carbon capture tax credit, while the faded bubbles are too small to be eligible. The total amount of CO2 emissions in Michigan is listed for each industry in million metric tons.
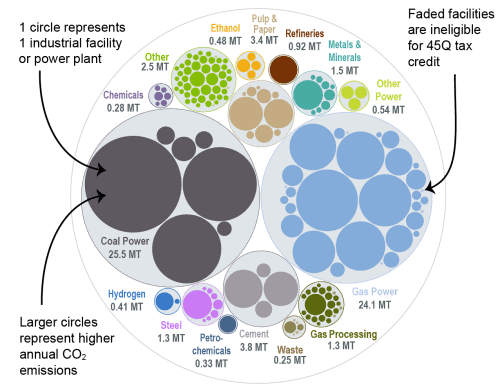
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024.
Last updated: May 2025

