Indiana Carbon Capture Opportunities

Carbon capture can lower emissions across a variety of sectors present in Indiana and bring jobs and private investment to the state. Of the 185 industrial and power facilities in the state, 146 are eligible for the 45Q federal tax credit. These 146 facilities emit nearly 98 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) annually, representing 99 percent of total annual CO2 emissions in the state.
Indiana has enacted some supportive legislation related to clean energy and carbon management deployment. However, the state could make significant progress in future legislative sessions to develop a supportive regulatory framework and fully realize the economic and environmental benefits of carbon management.
Industrial and Power Facilities in Indiana
Indiana has 146 facilities that are eligible for the 45Q tax credit. The state’s 19 gas power plants make up a large proportion, but the state’s highest emitters are its 13 coal power plants (coal plants that are slated for imminent retirement are not included in these figures). Combined, the emissions from Indiana’s eligible power plants represent 55 percent of the state’s total annual CO2 emissions. Indiana also has 28 metals and minerals facilities, 15 ethanol plants, 13 steel plants, six gas processing plants, and 52 other facilities that are 45Q-eligible. In total, all 146 facilities emit nearly 98 million metric tons of CO2 annually, representing 99 percent of the state’s annual CO2 emissions.
Indiana also has the potential to safely store captured CO2 underground in geologic formations across the state, including the Mount Simon Sandstone formation. Wabash Valley Resources was issued a Class VI injection well permit from the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2024 for its carbon capture and storage (CCS) project in Terre Haute. As of June 2025, Indiana has five Class VI applications under review with the EPA.
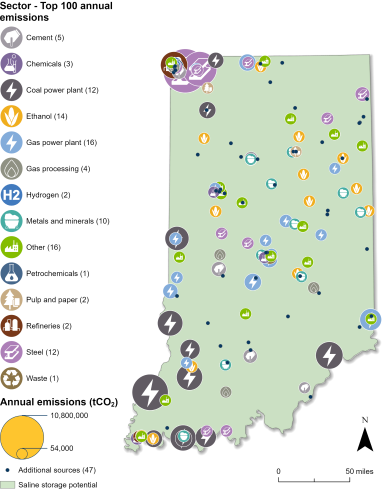
Sources: EPA GHGRP, 2024. Bauer et al., NATCARB, 2018.
Legislative Context for Carbon Management
Indiana’s legislative history demonstrates an understanding of the role carbon management can play in the state’s efforts to grow its economy and reduce emissions. The Comprehensive Hoosier Option to Incentivize Cleaner Energy (CHOICE) program was enacted in 2011 through SB 251, which was a voluntary effort that set a goal of 10 percent clean energy by the end of 2025. This bill also stated that it was in the public interest for the state to encourage the study, analysis, and development of CCS projects. SB 442, enacted in 2019, supports carbon capture as “a public use and service, in the public interest, and a benefit to the welfare and people of Indiana.”
Most recently, Indiana enacted SB 457 in 2025. This legislation specifies several requirements for CO2 pipeline and storage operators, including certain exemptions and required fees, and creates the Carbon Sequestration Project Program administrative fund.
In addition to enacted legislation, the state introduced several bills during the 2025 legislative session that did not pass before the session adjourned. To see details of this legislation, view our State Legislative Tracker.
This bubble diagram shows the number of facilities and corresponding annual CO2 emissions for each industry in Indiana. The darker, larger bubbles are eligible for the 45Q carbon capture tax credit, while the faded bubbles are too small to be eligible. The total amount of CO2 emissions in Indiana is listed for each industry in million metric tons.
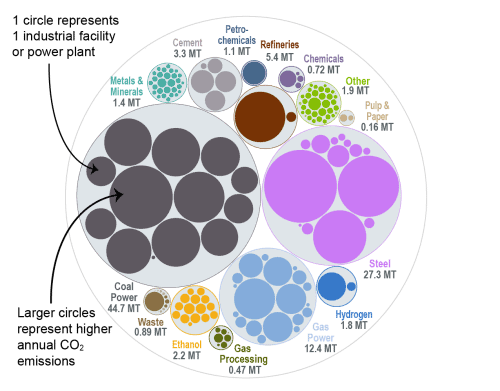
Source: EPA GHGRP, 2024.
Last updated: June 2025

